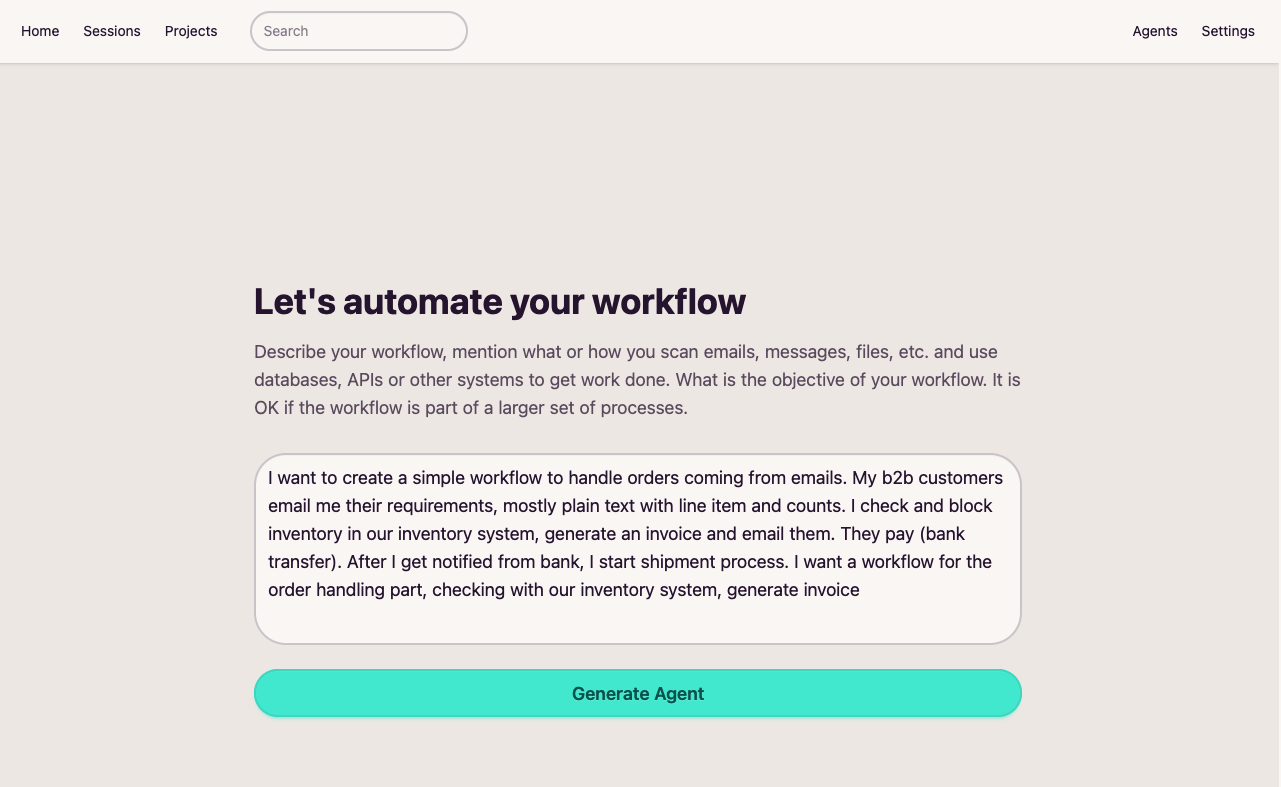
Define what your workflow should accomplish, and nocodo's AI agents work together to get it done. No coding required.

Specialized agents ready to handle your data analysis and document processing needs.
Query databases, explore codebases, and navigate file systems to extract insights.
Extract and process content from documents for analysis and workflow integration.
Choose the model that fits your needs for cost, speed, or capability.
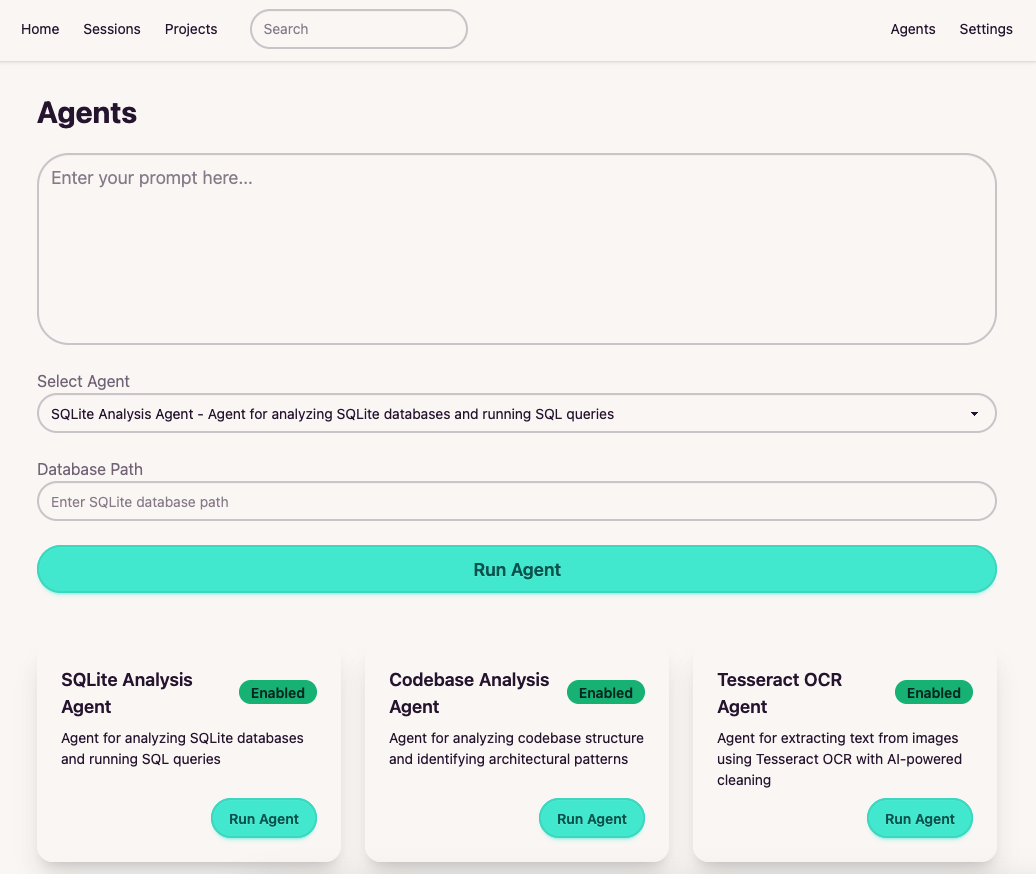
Multiple agents working together
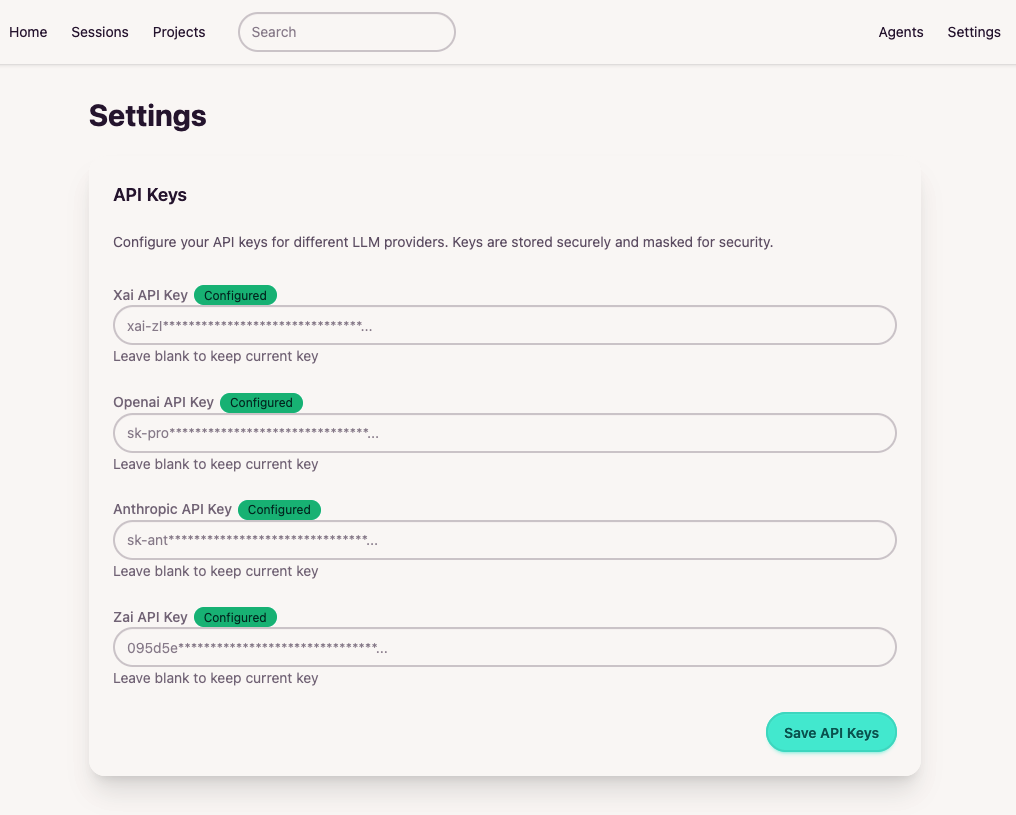
Choose from multiple AI providers
nocodo uses a multi-agent pattern where each agent is focused on a simple, specific objective and equipped with the tools it needs.
Break down a high-level goal into a Workflow with clear steps. Define what your workflow should accomplish in plain language.
Each step is assigned to a specialized agent with the right tools for the job. This keeps agents reliable and their outputs predictable.
Agents read data, extract information, compile answers, and respond. Complex workflows emerge from combining simple steps.
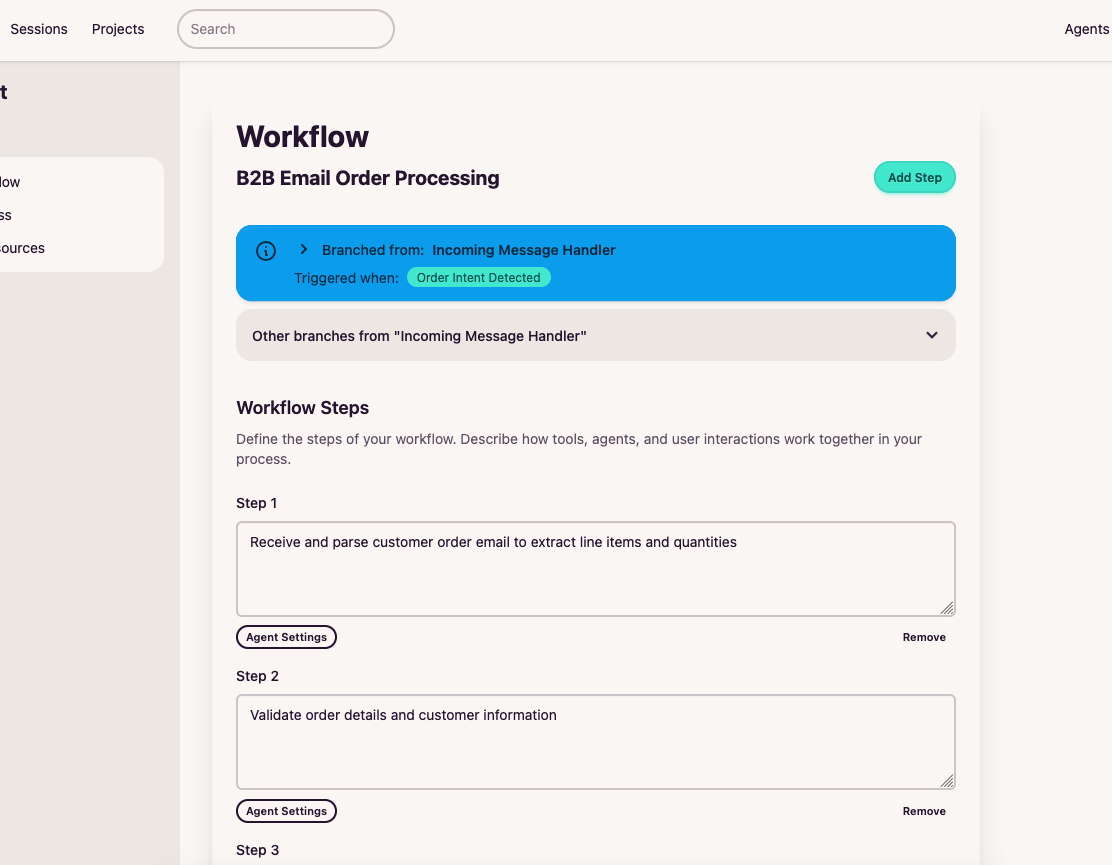
From internal automation to customer-facing operations.
Messaging integrations that allow nocodo to listen for incoming messages and trigger your agent workflows automatically.
Receive messages, process them with agent workflows, and respond automatically.
Additional capabilities to connect with external systems and generate outputs.
nocodo is self-hosted, giving you full control over your data and processes.
Deploy nocodo on your infrastructure
Configure your AI provider API keys
Use the GUI to create workflows
Let agents handle the work
Free and open source • Self-hosted • Full control over your data